Car tracking device is a unit which is installed into or on a vehicle, allowing a user or system to monitor its location.
The method in which the car tracking unit determines its position is through a GNSS system.
The most common GNSS system is known as the US Global Positioning System (GPS).

In addition, devices are not restricted to just GPS, as there are now the BeiDou, Galileo and GLONASS satellite systems available.
These GNSS systems can interoperate together, therefore providing superior signal coverage.
To determine the location of the tracker, it will communicate with satellites in orbit overhead.
By doing this, the tracker can receive current co-ordinates, which are then stored to the flash memory.
Later, at a designated interval the location is uploaded a GPS tracking server.
Therefore, upload intervals vary, depending on the application, and as a result it can be as quick as a few seconds, weeks or even months.
Generally the latter upload intervals would be for container freight or for agricultural purposes, where real time tracking is not critical.
Alternatively, a user receives co-ordinates by requesting the co-ordinates directly from the device through an SMS command.
The most common way that communication occurs between the tracker and the server is over mobile network.

Location data transfer methods
- Cellular/Mobile Network
- GPRS/SMS/CDMA/LTE
- Radio Frequencies
- Satellite Modem
- WiFim
Common Uses of a Car Tracking Device
The most common use for tracking a car is for cost savings, productivity enhancement, anti-theft and improved servicing scheduling.
Free or extremely low cost services may sell your tracking information to marketing companies for profit.
Workflow
Systems without a tracking server
This setup may work better for single users.
Once you have more than one gps device it will then become difficult to manage
- Device receives power (obd port, 12v wire, battery)
- Device searches for GPS signal, will sometimes use WiFi or Mobile Network assisted GPS to obtain GPS signal quicker
- GPS signal is found, location co-ordinates are obtained and stored in flash memory
- User sends SMS command to device
- Device responds with
i.) Co-ordinates of device
ii.) A map containing a pin where the device currently is.
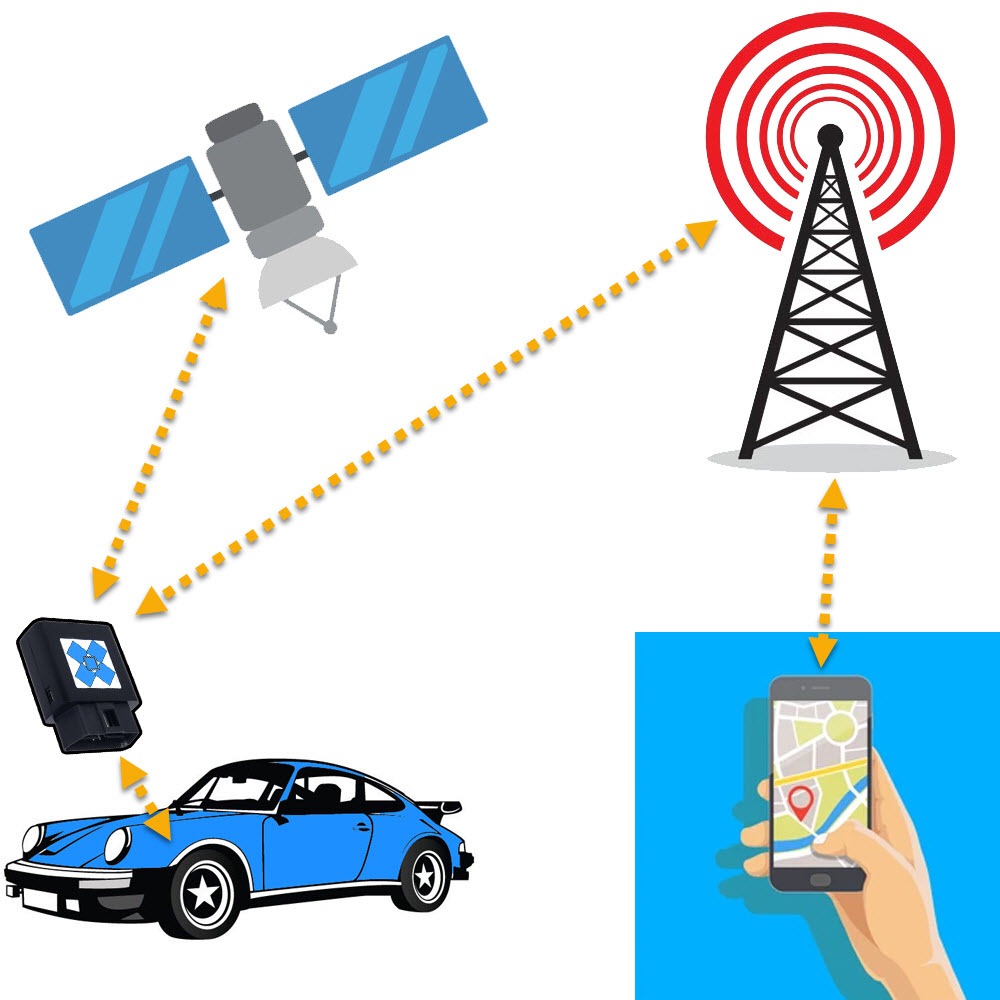
Systems with tracking server
The ideal solution for multiple cars that need to be tracked, therefore allowing you to view everything within the one portal/app.
- Device receives power (obd port, 12v wire, battery)
- Device searches for GPS signal, will sometimes use WiFi or Mobile Network assisted GPS to obtain GPS signal quicker
- GPS signal is found, location co-ordinates are obtained and stored in flash memory
- Location data is uploaded to server
- Server processes data and stores in database ready for viewing
- User interfaces with server with a website or application to view the location data on a map.
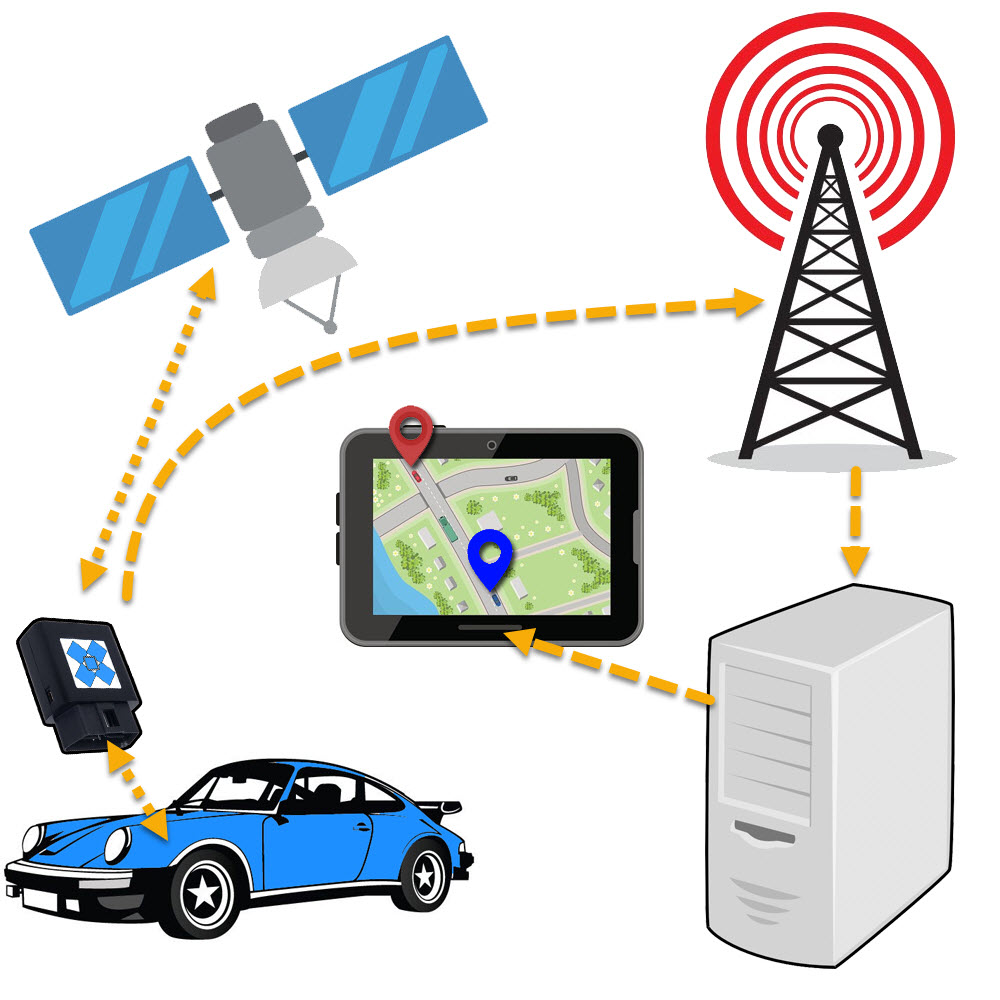
Segments Required
To use a car tracking GPS enable device, it requires multiple segments:
- Segment #1 GPS Tracking Unit
- Example: OBD Tracking Device
- Segment #2 GPS Tracking Server (not always necessary
- Example: GPYes Tracking Server
- Segment #3 User Interface
- Example: Tracking Portal or Android/iPhone app
- Mobile phone SMS
- Google Maps
GPS Tracking Unit / Car Tracking Device
The device fits into the vehicle in various ways, depending on the connectivity type.

Most tracking units in addition to providing the vehicle’s location data, feature a range of communication ports.
These ports are used to integrate other onboard systems.
In addition, other vehicle information that can be gathered include, but are not limited to:
- Fuel amount
- Engine temperature
- Latitude, longitude & altitude
- Doors open/close
- Tyre pressure
- Monitoring
- Battery status
- Fuel level
- Temperature by external sensors
- HDOP
- RSSI
- Computed odometer
- In rare cases, some vehicles can read odometer from ECU.
This depends on the vehicle manufacturer & the gps device manufacturer
- In rare cases, some vehicles can read odometer from ECU.
- Engine RPM
- Throttle position
You also have the ability to perform remote tasks such as;
- Fuel cut off
- Turn off ignition
- Turn on/off lights
- Listen in (if microphone enabled)
- Adjust tracking intervals
- Turn on/off the device
GPS Tracking Server
The tracking server has three responsibilities
- Receiving data from the GPS tracking unit
- Securely storing it within a database
- Serving this information on demand to the User Interface segment.
If you are sending SMS location request commands from the User Interface (ie. a mobile) this segment is not always required.
After an SMS location command is sent, a response is returned containing a map link.
User Interface:
The User Interface determines how the information is accessed.
Typical User Interfaces are
- Web portal (Browser based such as Internet Explorer, Safari, Chrome)
- iPhone Application
- Android Application
- Computer Program
Car Tracking Device Types
- OBD GPS devices
- Always plugged in
- Easy install
- Some can read additional CPU parameters and data
- Wired GPS devices
- Easier to hide
- Always wired in
- Can be connected to CANbus or additional sensors (temperature reading, RS232 inputs, R485 inputs)
- GPS devices that operate with a battery.
- Longer battery life
- Rechargeable
Common Features
- Real Time Tracking
- See the current location of your Trax GPS tracker in real time.
- Augmented Reality
- Quickly locate your Trax using the camera on your smartphone.
- Mobile Network Coverage
- 3G/4G Connectivity
- Custom Geofences
- Set digital fences and receive an alert as a tracker crosses the boundary.
- Alerts
- Overspeeds
- Device is unplugged
- Coolant temperature breaches a threshold
- Eexternal sensor temperate
- and more
- Multiple Device Tracking
- Multiple devices can be tracked at the same time
- Lightweight
- Small & Light, easily hidden.
- Multiple Viewing Interfaces
- Web portal, phone & web Apps
Car Tracker Legality
There are no Australian Federal Laws for surveillance and the use of tracking cars.
However, whilst there are no country wide laws, most individual states have their own statutes.
These statutes cover the use and restrictions of tracking devices used for surveillance.
For instance, the below states have formal statutes for the legality regarding the use of car tracking devices.
- Workplace Surveillance Act 2005 (NSW)
- Surveillance Devices Act 1998 (WA)
- Surveillance Devices Act 1999 (VIC)
- Workplace Privacy Act 2011 (ACT)
- Surveillance Devices Act 2007 (NT)